Asia Certification
Global certification:
China CCC Certification: China CCC certification (CCC), which covers Safety and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) and has factory inspection requirements. Products in the CCC certification list need to obtain the CCC certificate before they can be sold in China.

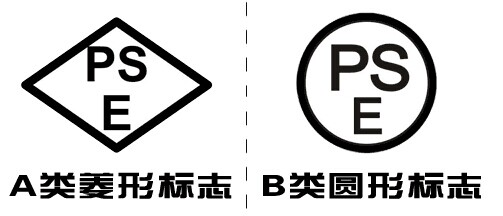
Japan PSE Certification: PSE certification is Japan's mandatory safety certification, diamond-shaped PSE and circular PSE certification.
According to Japan's Electrical Product Safety Law (NENAN),457 products must pass PSE certification to enter the Japanese market. Among them, 116 Class A products are specific electrical appliances and materials, which must be certified and affixed with PSE (diamond) logo on the products. 341 Class B products are non-specific electrical appliances and materials, which must be self-declared or apply for third-party certification. And identify the PSE(circle) logo on the product.
Diamond-shaped PSE certification has factory inspection requirements, circular PSE certification has no factory inspection requirements.
Japanese MIC TELEC certification: Japanese MIC certification actually refers to the popular said more TELEC certification, from the professional point of view, Japanese MIC certification is called more professional. MIC certification is a necessary certification for model approval of radio equipment and a mandatory certification for wireless products to enter the Japanese market. It has no requirements for factory inspection, but requires ISO certificate or approved quality control documents. In MIC certification, MIC refers to the MIC of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications of Japan. MIC supervises the Radio Law and the Electrical Telecommunications Business Law of Japan. In the previous certification industry, the radio wave method is called TELEC certification, and colloically speaking, MIC certification is equivalent to TELEC certification
Japan's Radio Regulatory Commission Rules No. 18 require type approval (certification of technical regulatory compliance) for designated radio equipment. MIC TELEC certification is mandatory and the certification body is the registered certification body recognized by MIC in the specified range of radio equipment. TELEC (Telecom Engineering Center) is the main registration authority for radio equipment compliance certification in Japan.
KC Safety Introduction:
Korea KC mark certification, is a mandatory safety certification system in South Korea. According to the requirements of the latest "Electrical Appliances Safety Management Law", KC Safety certification is divided into three categories according to the different levels of product harm: Mandatory Safety Certification, Self-regulatory Safety Confirmation, Supplier Self- confirmation. From January 2009, all products within the mandatory range will be required to obtain a KC certificate.
Safety certification: South Korean test and certification, the need for factory inspection, certificate continues to be valid;
Safety confirmation: Korea test and certification, no need for factory inspection, the certificate is valid for 5 years;
Supplier self-confirmation: Supplier self-confirmation

KC EMC and RF Introduction:
KC EMC and KC RF certification includes electromagnetic compatibility testing, radio frequency and telecommunications testing. According to the requirements of the latest Chapter 58-2 of the Radio Wave Law, the certification system is divided into three categories according to the different levels of harm to the radio environment: Certification of Conformity, Registrationof Compatibility and Interim of Conformity.

BIS (Bureau of Indian Standards) Certification:
The subject of application for BIS certification is the manufacturer/factory. At present, there are 30 types of controlled products. Controlled products must be tested to specified standards and registered in officially authorized and accredited laboratories in India. In addition, the product can enter the Indian market only after the certification mark is marked on the product body or the outer packaging box. Otherwise, the goods will not be able to clear the customs.


Indian WPC certification: The full name is Wireless Planning and Coordination Wing, is India's wireless regulation agency, all wireless products must be approved by WPC before entering the market. The wireless certification of the wireless product in India can be divided into two modes: Equipment Type of Approval (ETA) and License. The decision is based on the working frequency band used by the application equipment. For free and open frequency bands, ETA certification is required. If the device uses other bands that are not freely available, such as GSM and WCDMA phones, it will need to apply for a license.

India TEC Certification:
The Centre for Telecommunication Engineering, Ministry of Telecommunication of the Government of India, issued the formal compulsory notice of TEC Certification on 12 March 2019, which stipulates in the Operational Procedure for Compulsory Testing and Certification of Telecommunication Equipment (MTCTE) that all telecommunication equipment will be officially compulsory from 1 August 2019. At that time, telecom equipment that is not certified by the TEC will not be able to be sold in the Indian market, or face heavy fines and removal penalties.
The certificate of TEC certification is valid for 5 years, which needs to be held by the factory and the information of the local representative in India needs to be provided. Some telecom products need to be sent to the local laboratory in India for testing.
Thailand TISI Certification:
TISI is a compulsory certification stipulated by the Royal Decree of Thailand, which stipulates that the electronic and electrical products involved must meet the TIS standard of Thailand and be labeled before they can be legally sold in the Thai market. Currently, only locally registered companies in Thailand can be licensed, and samples need to be sent to local laboratories in Thailand for testing.

Thailand NTC Certification:
The NTC is the body that regulates wireless and telecommunications regulations in Thailand, and all wireless and telecommunications products must be licensed by the NTC before entering the market. Only locally registered companies can act as NTC holders. NTC applications are classified into Class A, ClassB, and sDoC by product classification.
Class A products must be tested in the laboratory designated by NTC, and get the login number and certification certificate after providing the data required by NTC, which needs to be matched with samples.
The Class B certification procedure is consistent with the Class A product category. Only foreign reports such as FCC/CE/CB can be used for the certification application of the transfer mode. The landing number and certification certificate must also be obtained.
sDoC product certification is voluntary. The sDoC form should be filled out by the customer's local representative in Thailand and sent to NTC for reference together with the technical data documents. No sample is required.

Taiwan BSMI certification:
BSMI (Taiwan Bureau of Standards and Inspection) is an official agency under the Ministry of Economic Affairs of Taiwan. It conducts commodity inspection and certification in accordance with the "Commodity Inspection Law" (mandatory requirements) and the "Standard Law" (voluntary requirements). The products involved in the "Commodity Inspection Law" must pass the certification before they can be sold in the Taiwan market.
The holder of BSMI should be a local legal company in Taiwan, and manufacturers in other regions can apply through Taiwan dealers.




